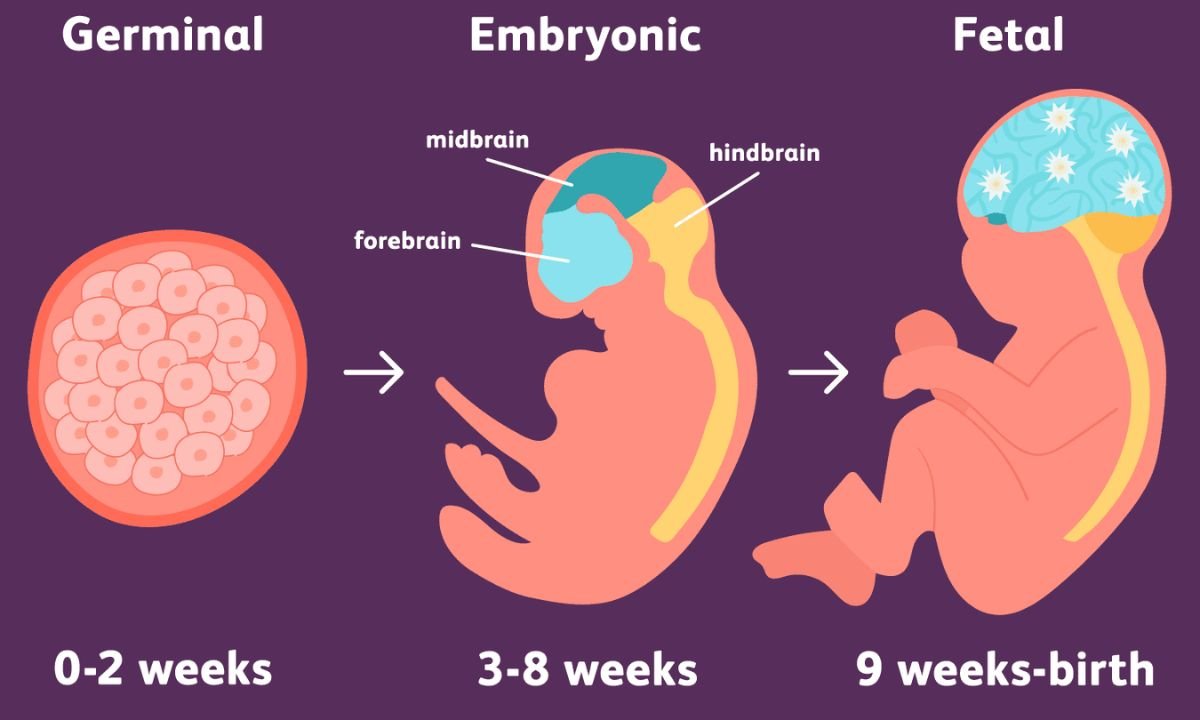
Human life begins in a remarkable and intricate process that unfolds within the womb. Have you ever wondered how a single cell transforms into a fully formed baby? The journey from conception to birth is fascinating, filled with complex stages and rapid changes. Understanding the early stages of life can provide insights into human development and the factors that influence it.
Embryonic development refers to a human embryo’s stages, from fertilization to becoming a fetus. This process is crucial as it lays the foundation for all the body’s organs and systems. This article will research the different stages of fetal development, highlighting key features and milestones that occur during each phase.
Fertilization and the Beginning of Life
Fertilization marks the starting point of human life. It occurs when a sperm cell successfully merges with an egg cell, creating a single cell known as a zygote. This union results from a complex process involving ovulation, sperm travel, and fertilization.
Once fertilized, the zygote begins to divide, embarking on its journey of growth and development. This stage is crucial as it determines the genetic blueprint of the individual.
Cleavage and Blastocyst Formation
After fertilization, the zygote experiences a series of rapid cell divisions known as cleavage. These divisions continue as the zygote travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. By reaching the uterus, it has transformed into a cluster of cells called a blastocyst.
It consists of an inner cell pile that eventually develops into the embryo and an outer layer of cells that forms the placenta. This stage is essential as it prepares the embryo for implantation in the uterine lining.
Implantation and Early Development
Implantation is a critical step in the early stage. The blastocyst connects itself to the uterine lining, where it will receive nutrients and oxygen necessary for its growth. During this stage, the inner cell mass differentiates into three primary layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Each layer will ascend to different tissues and organs in the developing embryo. Implantation is a crucial milestone as it secures the embryo’s position within the uterus, allowing further development.
Gastrulation and Germ Layer Formation
Gastrulation is a significant phase in which the three primary germ layers are ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This process sets the stage for organ development, with each layer specializing in various tissues and systems:
- Ectoderm: Progresses into the skin and nervous system.
- Mesoderm: Gives rise to muscles, bones, and the circulatory system.
- Endoderm: Grow into the digestive and respiratory systems.
Neurulation and the Formation of the Nervous System
Neurulation is the stage during which the nervous system begins to form. The ectoderm layer folds to create the neural tube, which later advances into the brain and spinal cord. This stage is critical for developing the central nervous system, and disruptions can lead to severe congenital conditions.
Organogenesis and the Development of Major Organs
Organogenesis is the phase where significant organs start to form. This process begins with the differentiation of the germ layers into specific tissues and organs. For instance, the heart begins to beat around the third week of development, and other organs, such as the liver, lungs, and kidneys, begin to take shape. By the end of this stage, the embryo has developed a rudimentary structure resembling a miniature human.
Fetal Development and Growth
Following organogenesis, the embryo enters the fetal stage, and it is called a fetus. During this stage, the body systems formed during the embryonic phase continue to develop and mature. The fetus proliferates in size, and its organs become fully functional. The fetus’s development during this period is critical for survival outside the womb.
Embryonic development is a complex and dynamic process that lays the foundation for human life. Correctly understanding this process sheds light on human development and highlights the importance of fertility and reproductive health. As science continues to reveal the mysteries of fetal development, it provides valuable insights that can improve medical practices and outcomes for future generations.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Options for Managing Varicose Veins: A Comprehensive Guide